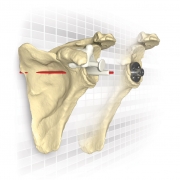
AltiVate Reverse®
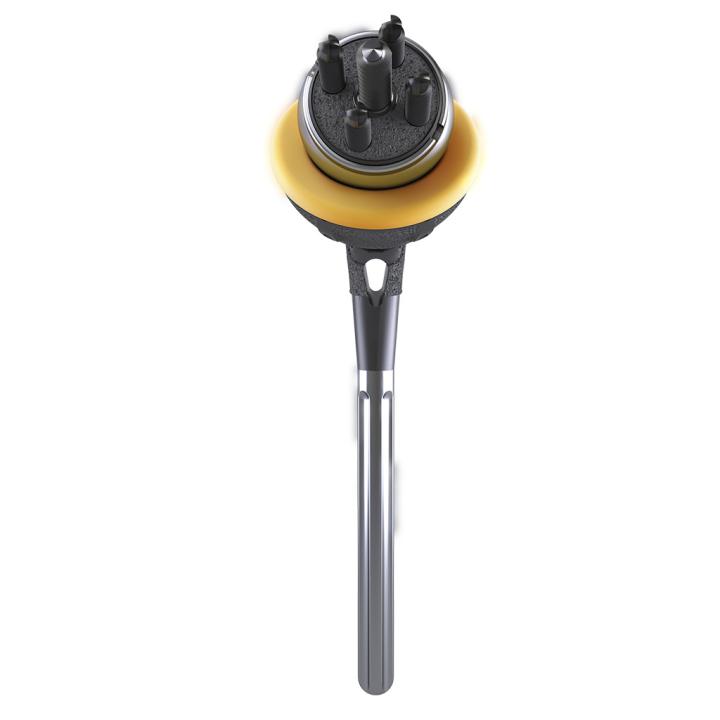
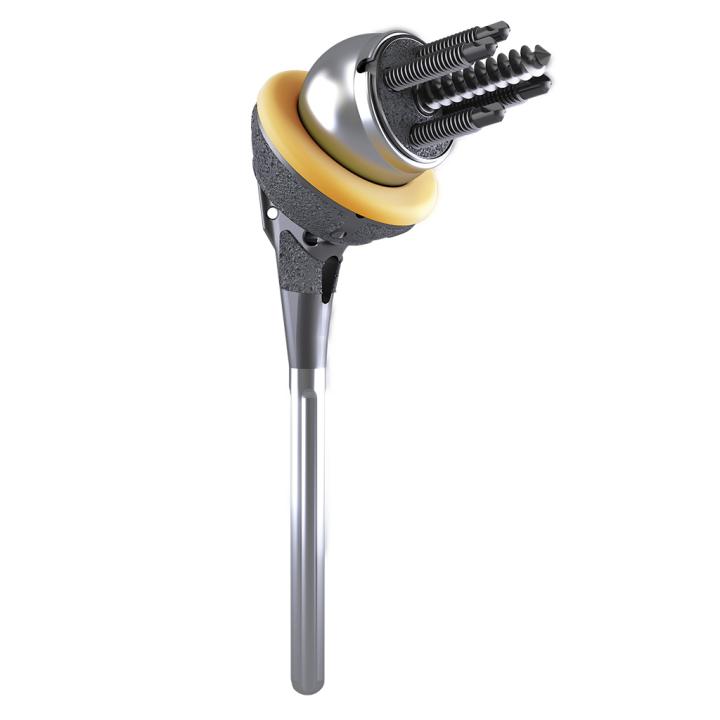
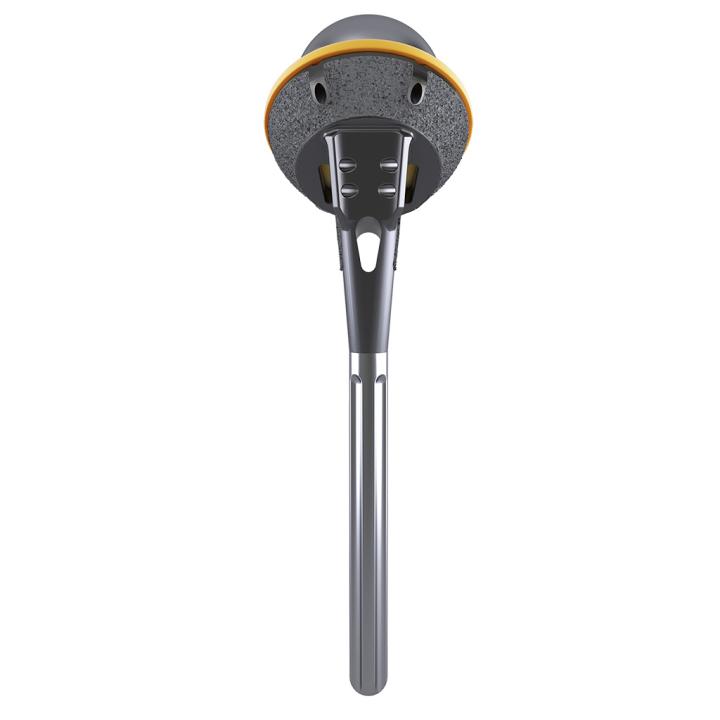
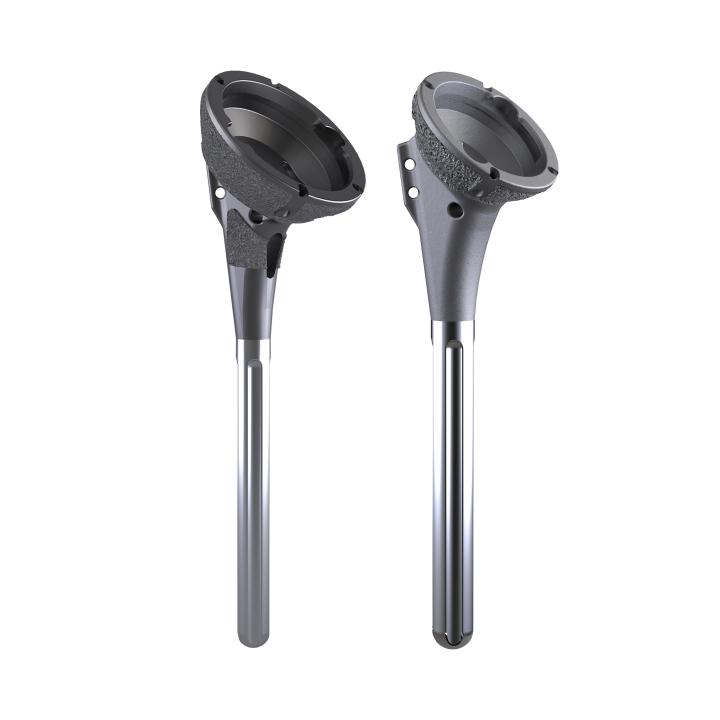
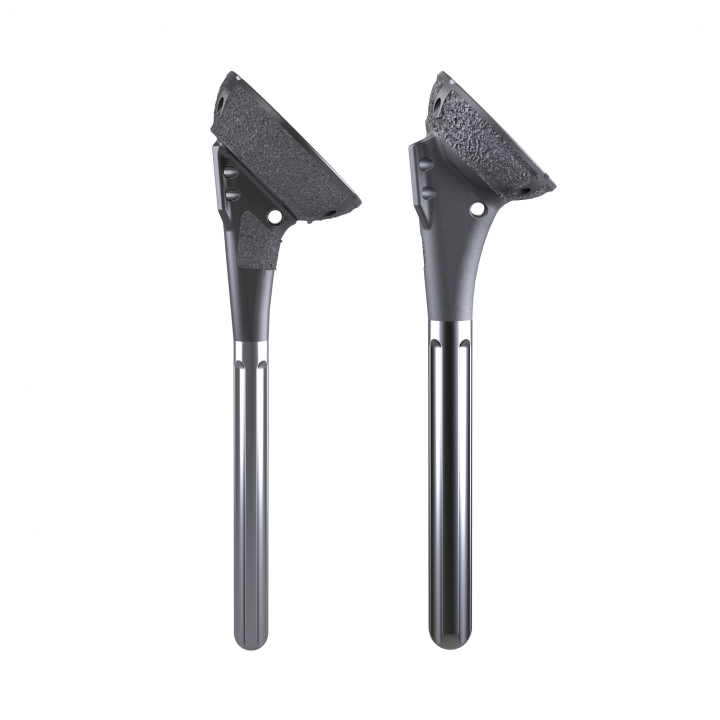
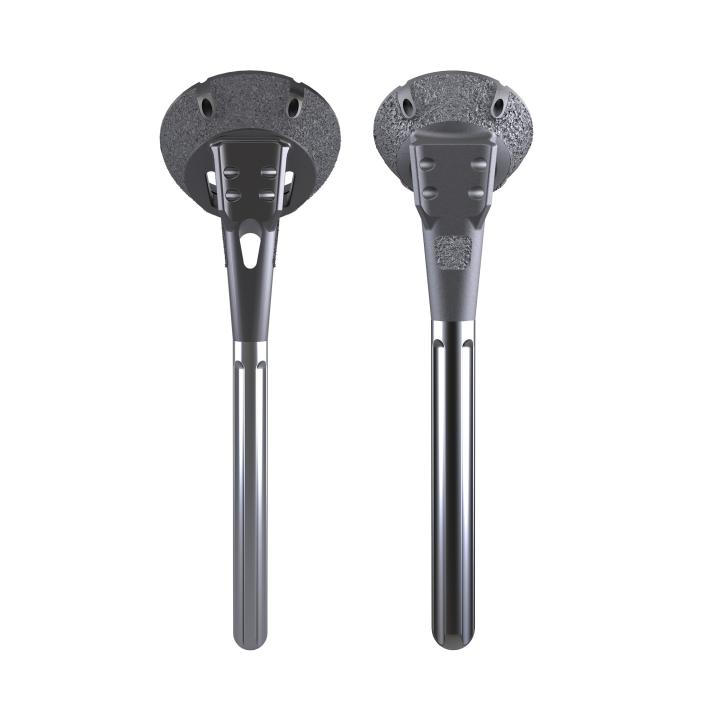




















AltiVate Reverse®
Revolutionary or Proven? BOTH.
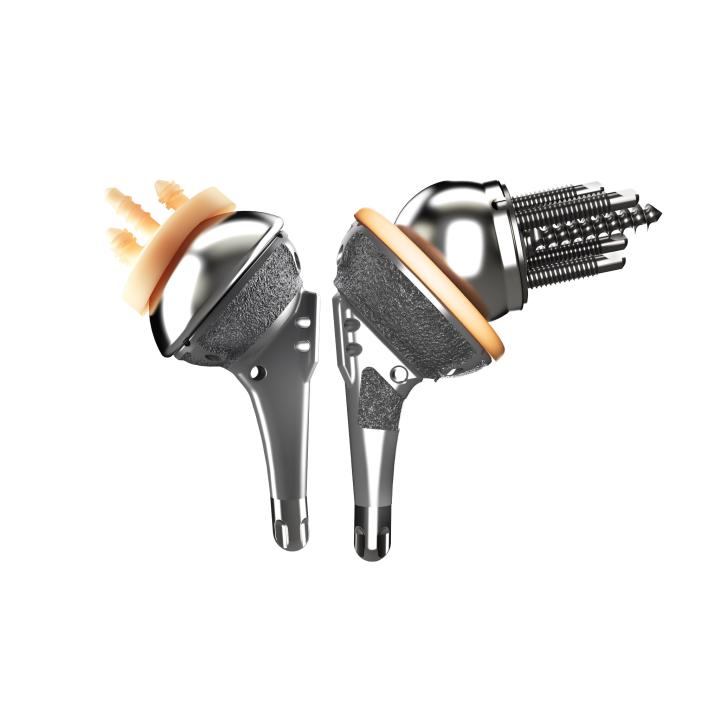
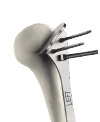
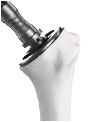
AltiVate Reverse® is built solely on the first-to-market and only 135° stem to be backed by 10 years of proven clinical data showing no decline in patient outcomes.8 With streamlined instrumentation and fully interchangeable stem and glenosphere sizing, the AltiVate Reverse system is the simple choice to meet the needs of today’s surgical environments.
These design principles include a center of rotation lateral to the glenoid, the first to market humeral neck angle of 135°, and a humeral stem inlaid within the humeral bone. The 48mm stems are the first short, convertible, inlay stems on the market.
With indications for reverse TSA, anatomic TSA, and hemiarthroplasty (including proximal humerus fractures), AltiVate Reverse® is one platform to treat your arthroplasty patients. With four different stem length options (48mm, 108mm, 175mm, and 220mm) and two different shell sizes (36mm and 42mm), the AltiVate Reverse® system has options to meet the needs of patients across a wide spectrum of humeral anatomies.
- Overview
- Videos
- Related Products
- References
Features & Benefits
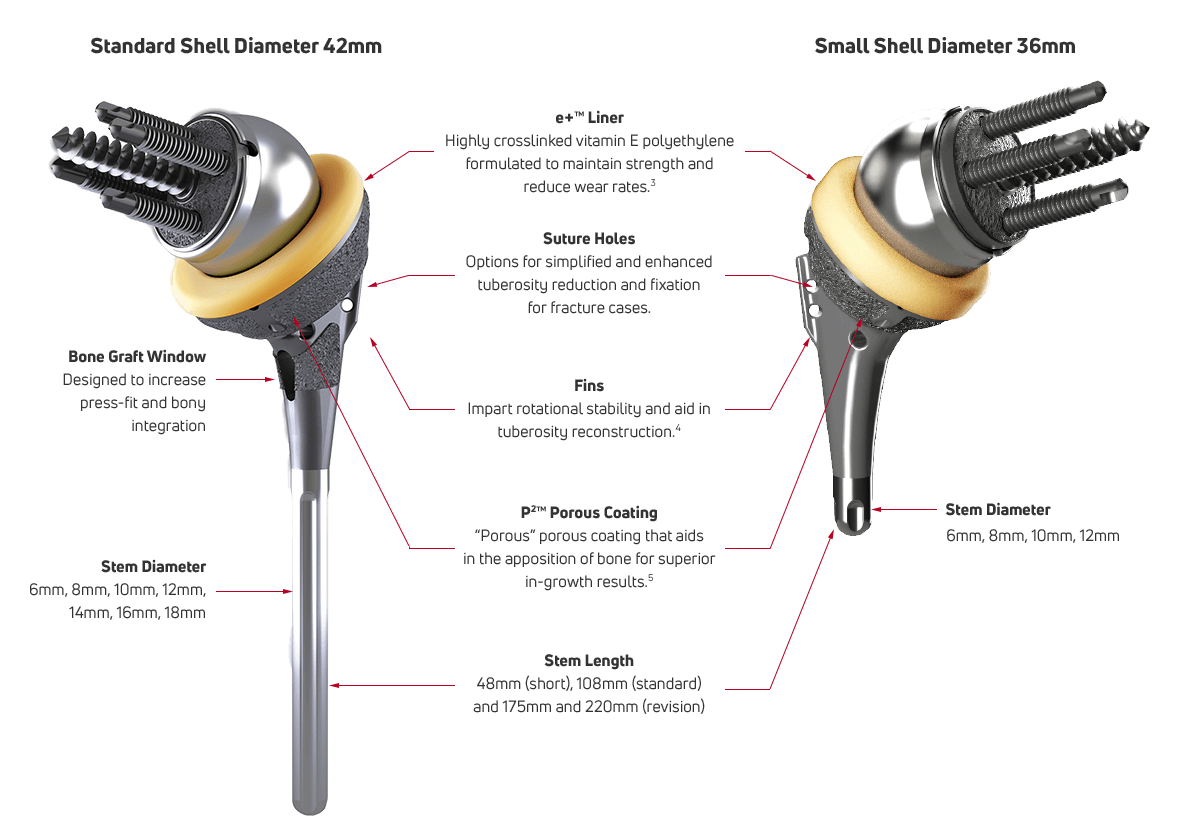
Enhanced Fixation
 Our one piece, monolithic AltiVate Reverse® glenoid baseplate design provides 2000N or 10X more compression than a pegged baseplate design,7 providing stable initial fixation. On both the glenoid and humeral components, our proprietary coating, P²™, aids in the apposition of bone for superior bony ingrowth.
Our one piece, monolithic AltiVate Reverse® glenoid baseplate design provides 2000N or 10X more compression than a pegged baseplate design,7 providing stable initial fixation. On both the glenoid and humeral components, our proprietary coating, P²™, aids in the apposition of bone for superior bony ingrowth.
P2, backed by the largest porous coating animal study in the world also creates instant micro-fractures in the trabeculae upon initial bite to the bone, which causes an instantaneous bone in-growth reaction.2
Clinical Application
The AltiVate Reverse® is indicated for a variety of applications:
- Anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty
- Hemiarthroplasty
- Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty
- Hemiarthroplasty for fracture
- Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for fracture
For each of these applications, the stem can be cemented or press-fit.
Anatomic Basis
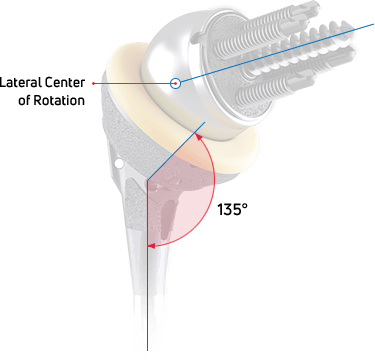
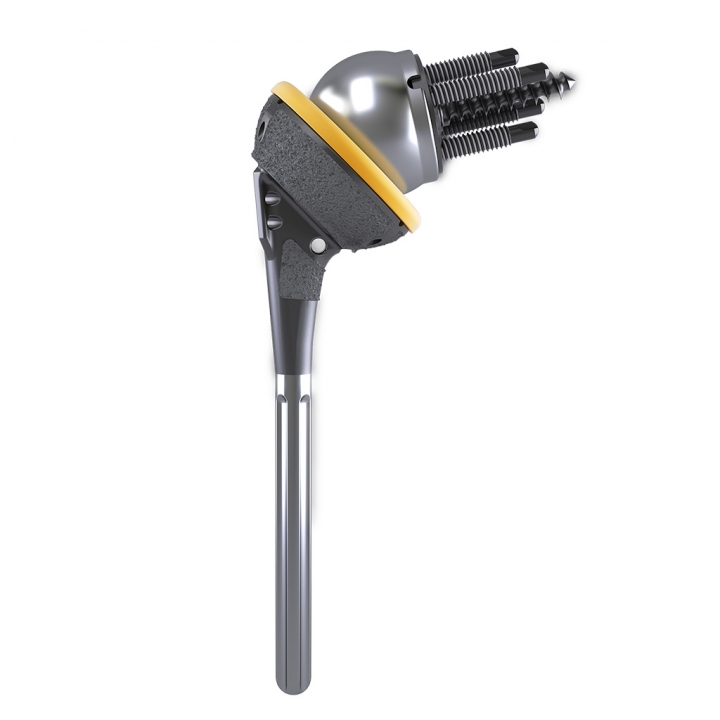
The AltiVate Reverse® stems were designed using anatomic studies to optimize the shell-to-stem position and to match patient anatomy for both anatomic and reverse total shoulders. This design features an anatomic humeral neck-shaft angle of 135°.
Biomechanical testing has shown that having a humeral neck-shaft angle in the range of normal anatomy reduces the potential for inferior scapular notching.6
Versatility for Complex Anatomy
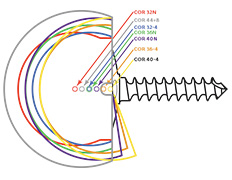
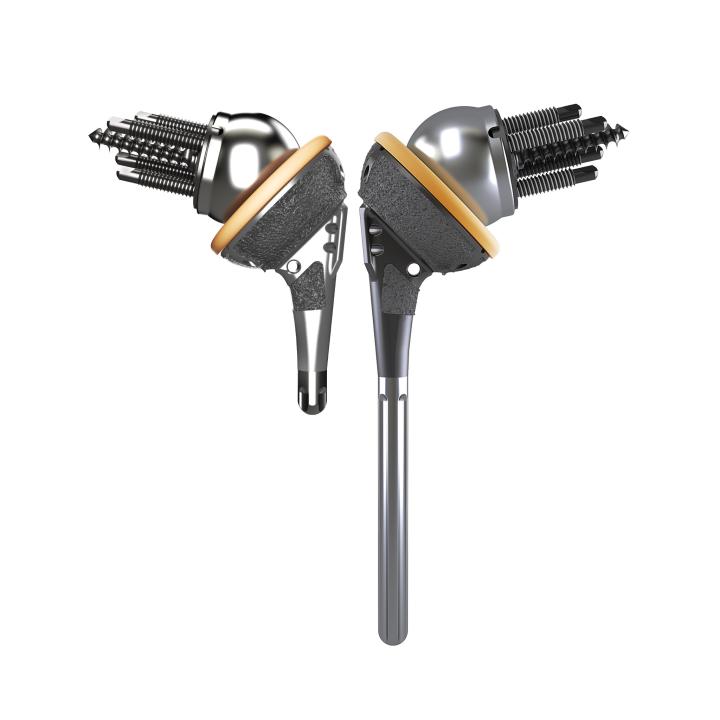
Glenospheres
A great deal of variability can be experienced in rotator-cuff-deficient shoulders. The AltiVate Reverse® system offers unmatched versatility, in size and offset, of glenospheres to manage complex anatomy and surgical outcomes.

Socket Inserts
Both traditional and +4mm inserts are available in 32, 36, 40 and 44mm in standard and semi-constrained providing various options of height, diameter, and constraint.
These options are also available in our highly-crosslinked, Vitamin E-blended e+™ poly. Learn more about it here.

Metal Spacers
This 8mm Spacer is screwed into the standard AltiVate Reverse® Stem and with a traditional insert provides 8mm of humeral prothesis build-up.
The AltiVate Reverse® Small Shell Stem has both 8mm and 12mm metal spacers for additional build-up options.

Hemi-Adapter
This Hemi-Adapter is screwed into the AltiVate Reverse® Stem and with a Turon® or AltiVate® Anatomic humeral head converts the reverse stem to a hemi-arthroplasty prosthesis.
This implant is available with both the Standard and Small Shell versions of the AltiVate Reverse® stem.
Precision Instrumentation
The AltiVate Reverse® instrumentation was designed for two different surgical approaches, catering to different surgical preferences. The instruments simplify prosthesis positioning and implantation, and specialized revision instruments allow for stem removal with minimal bony disruption.
Metaphyseal-Referenced
Implant position is based on the fit in the metaphysis.
Osteotomy

Create centered
pilot hole

Protect and
move to glenoid
Ream Socket

Ream Canal

Assemble trial
shell and broach

Impact trial assembly
Diaphyseal-Referenced
Implant position is based on the fit in the humeral canal.

Osteotomy

Ream Canal

Broach

Protect and move
to glenoid

Add reaming /
planing guide pin

Plane

Ream Socket

Insert socket trial

AltiVate Reverse® Surgery

AltiVate Reverse® Surgical Technique Animation

AltiVate Reverse® Short Stem Animation

RSA Glenoid Bone Graft Surgical Technique with Dr. Jonathan Levy

Dr Levy AltiVate Reverse for Fracture Presentation
- Data on file at DJO®. Laboratory testing does not necessarily indicate clinical performance.
- Cuff DJ, Pupello DR, Santoni BG, Clark RE, Frankle, MA. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of rotator cuff deficiency: a concise follow-up, at a minimum of 10 years, of previous reports. J Bone Joint Surg 2017; 1895-1899.
- Data on file at DJO®. Laboratory testing does not necessarily indicate clinical performance
- Data on file at DJO®. Laboratory testing does not necessarily indicate clinical performance.
- Beck, J.P. et al. Bone Response to Load Bearing Percutaneous Osseointegrated Implants for Amputees: A Sheep Amputation Model. 56th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society. Poster #2085. March 2010.
- Gutierrez S, Comiskey CA, Luo ZP, Pupello DR, Frankle MA. Range of impingement-free abduction and adduction deficit after reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Hierarchy of surgical and implant-design-related factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:2606-15.
- Frankle MA, Virani N, Pupello D, Gutierrez S. Rational and Biomechanics of the Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis: The American Experience in Rotator Cuff Deficiency of the Shoulder. Thieme. 2008
- Cuff et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of rotator cuff deficiency: a concise follow-up, at a minimum of 10 years, of previous reports. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2017